How seriously do institutions take their role in creating a more equal, fair and just world? As well as environmental impact, the QS Sustainability Rankings also considers university impact around today’s biggest social issues.
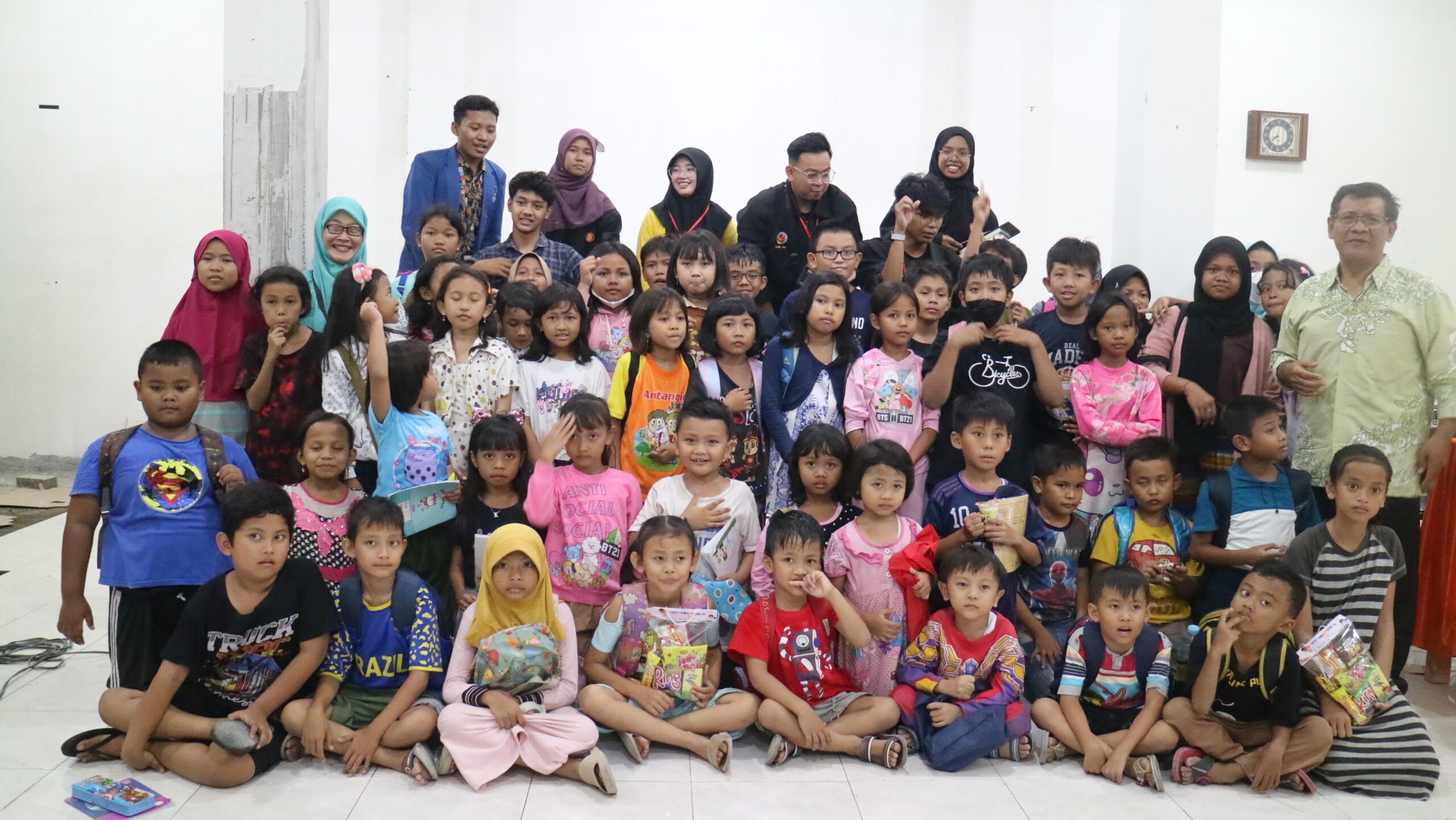
The equality indicator rates institutions according to a number of factors, such as the percentage of female faculty and students, the accessibility of public equality, the diversity and inclusion policy, and the accessibility of disability support.
The knowledge exchange indicator evaluates universities’ tendency to collaborate with other organizations and institutions as well as their dedication to sharing information in partnership with institutions that receive less financial assistance.
Impact of education examines the university’s research on high-quality education, the impact of its graduates on the community and its academic standing in pertinent social issues, as well as how free students and academics are to conduct research without interference.
Based on how well-prepared students are for successful professions, the employability and opportunity indicator assigns each university a score for the employer reputation and a score for employment outcomes. Universities are also graded on their research into employment and economic development, as well as peace, justice, and strong institutions, as well as the unemployment rate in the nation in which they are located.
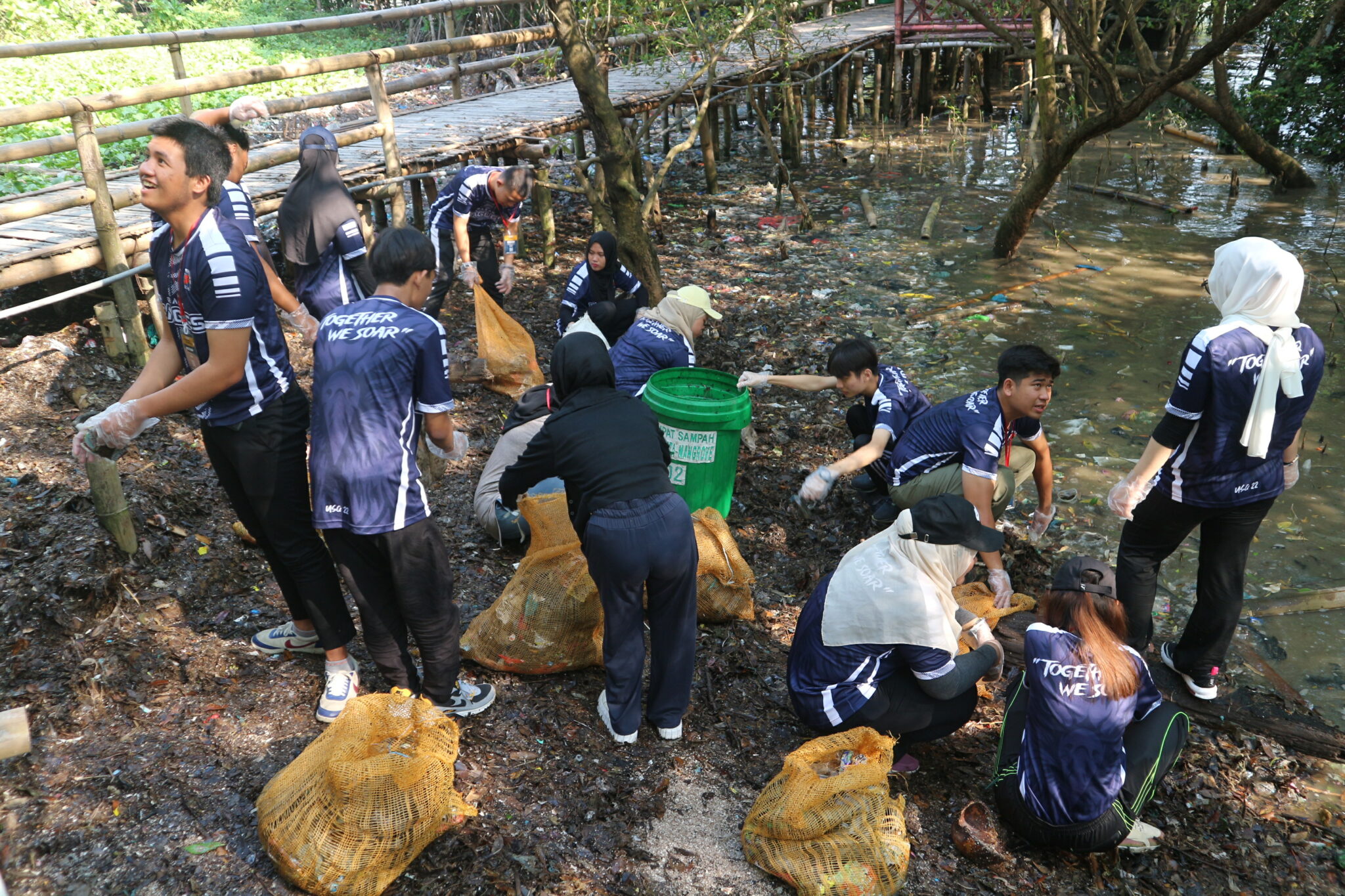
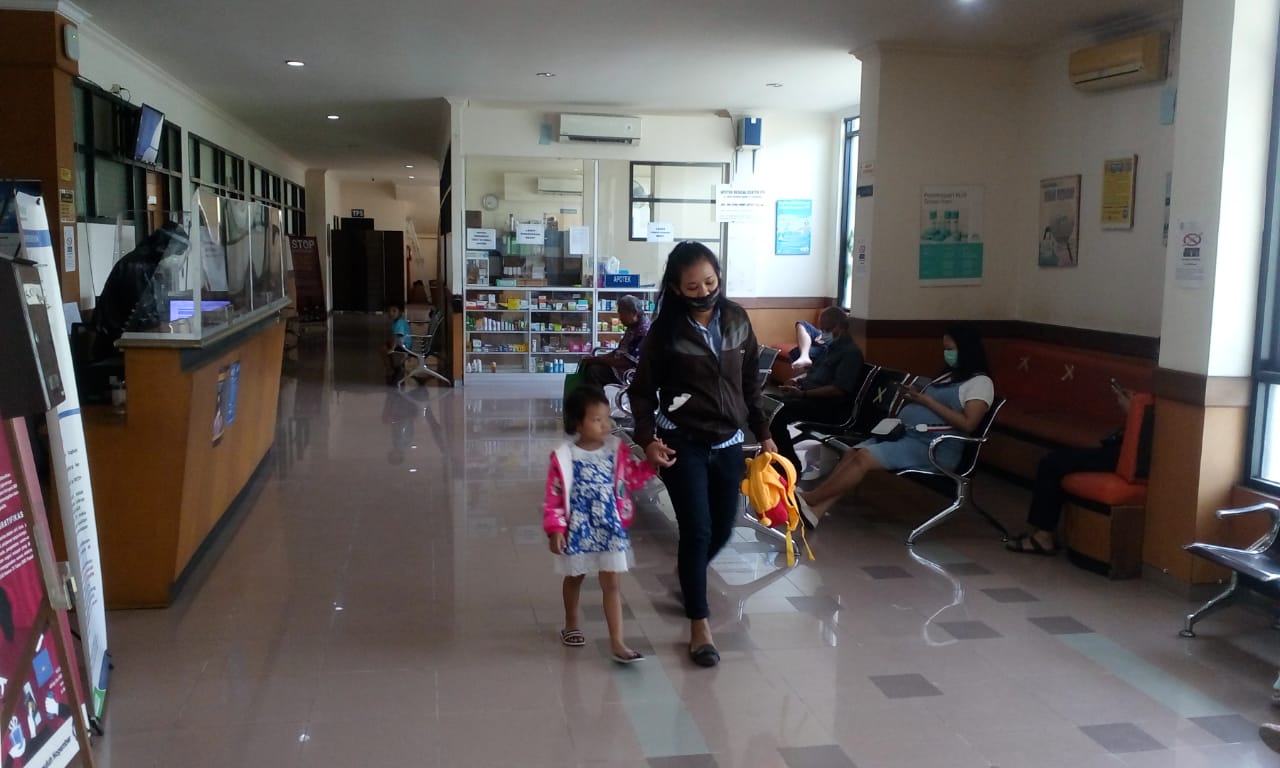
The last social effect measure, quality of life, is used to assess how committed a given institution is to overall wellness both inside and outside the university. We also take a look at studies being done, for instance, on the region’s air quality, campus health services, and quality of life.