The Civil Engineering Department is under the Faculty of Civil, Environmental, and Geo-Engineering (FTSLK) Ten November Institute of technology (ITS) Surabaya. Civil engineering had the vision to become the Centre of reference (Resource Center) in civil engineering in Indonesia which support the development of the marine industry and environmentally.
Field of Study
Undergraduade Program (S1)
Download Curriculum for Undergraduate Program here
Expected Learning Outcomes
Indonesia government has published Presidential Regulation No. 8/2012 about Indonesian National Qualification Framework (INQF) as a national guidance for the formulation of the graduates Expected Learning Outcomes (ELO). This gives an understanding that each student should possess the same standard of competence . An undergraduate program should set its learning outcomes so that graduates must achieve at level 6 of INQF. According to this Regulation, ELO is ability that can be obtained from accumulated working experiences, knowledge, managerial abilities and attitudes.
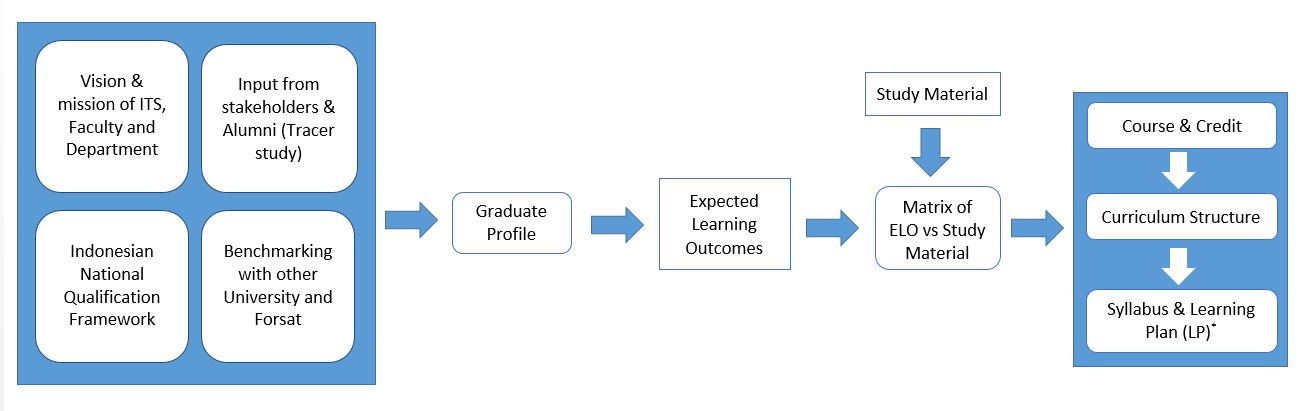
The DCE ELO is formulated based on Graduates’ Profile which derived from vision and mission of ITS, Faculty and Department, INQF, Stakeholder and Alumni Input, and Benchmarking with Best Practice of National and International Universities. According to long discussion with DCE academic members, the DCE graduates’ profile defines as: “Produces engineering graduates who are able to work cooperatively in group to design environmentally sustainable Civil Engineering infrastructures, and to have enterpreneur skills, as well as to have enough knowledge to improve themselves based on the philosophy of lifelong learning.”
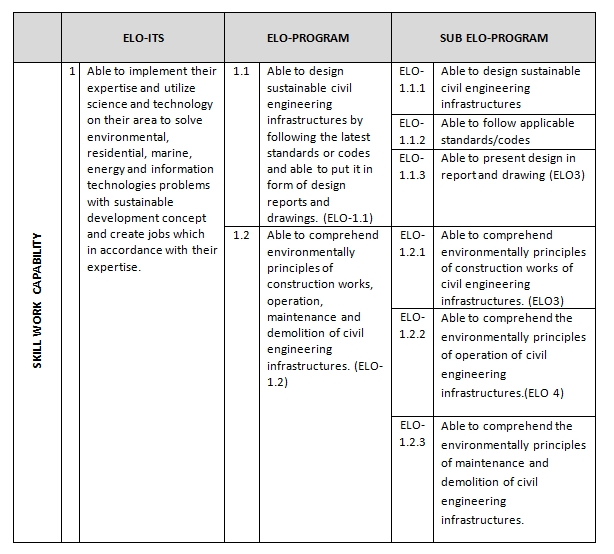
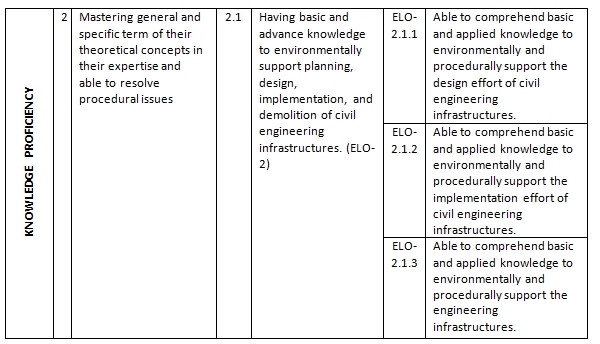
In addition to core competencies that become a primary identifier of DCE graduates, it was also defined in ELO about supporting competence and specific competencies in accordance with core competencies. Elements of competence in every subject may include grounding aspects of personality, mastery of knowledge and skills, ability to work, attitudes and behaviors in the work, and understanding the rules of life and society. The profile is derived from 4 main ELO with 12 sub-ELOs and expected to be possessed by graduates of DCE-ITS. Based on the ELO, DoS prepared the structure and content of the curriculum in order that the required competencies should be achieved.
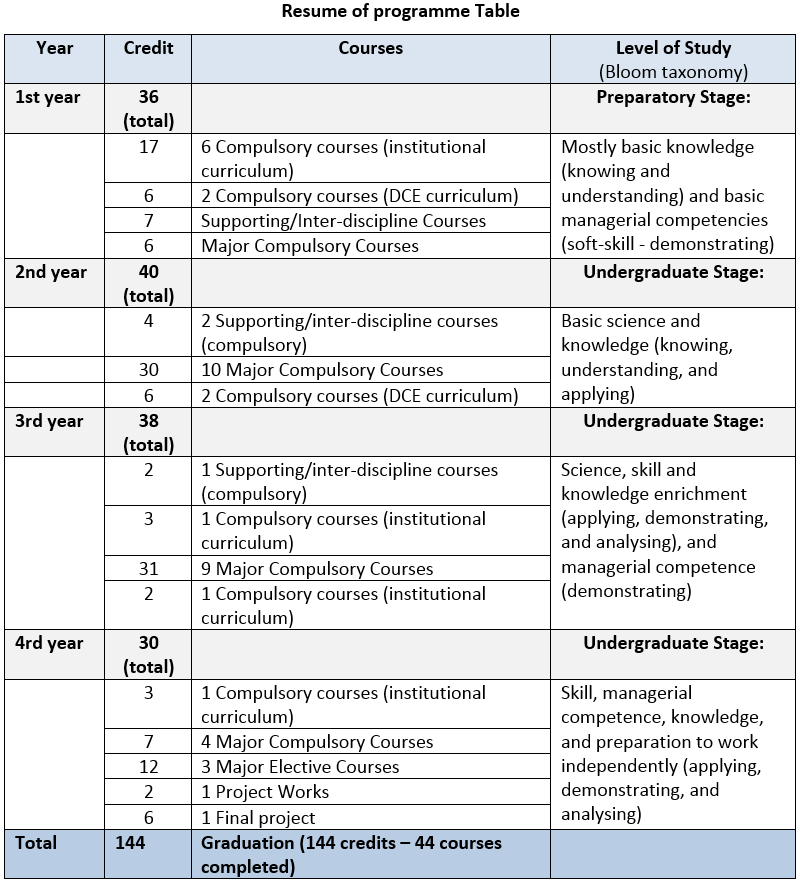
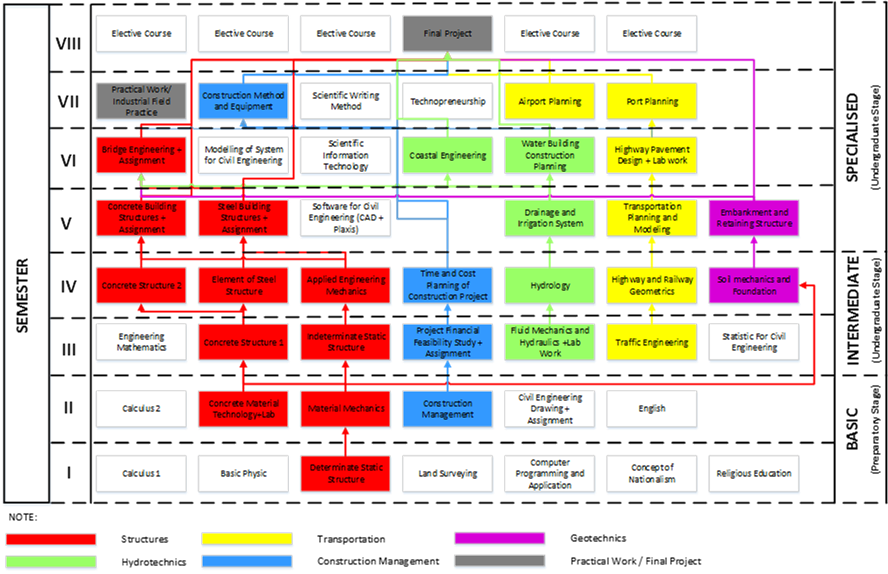
Undergraduate/bachelor programme (2014-2019 DCE curriculum) is divided into 2 stages: 1. preparatory stage with load of 36 credits (conducted in 2 semesters), and 2. undergraduate stage with load of 108 credits (6 semesters). The total 144 credits of programme (48 subjects) consist of 45 compulsory subjects (132 credits) and 3 elective subjects (12 credits). The compulsory subjects consist of compulsory subjects in preparatory stage, major compulsory subjects including final projects and project works, and supporting/interdiscipline subjects. In preparatory stage, compulsory subjects include fundamental science and engineering subjects which support DCE curriculum, and soft skill subjects which are taught in all faculties based on institutional curriculum (ITS curriculum). In preparatory stage, the programme focuses on developing generic skills and knowledge. Thus, soft skill subjects are designated to prepare and equip the first year students with academic professional ethic and attitudes. The generic skill and knowledge of student is then strengthened in undergraduate stage by completing supporting subjects. Therefore, 34.7% of subjects in the programme is designed to develop generic skills and knowledge, while 65.3% of subjects is structured to develop specialised skill and knowledge (Major compulsory, elective courses and final projects).
Major compulsory subjects are categorized into 5 core modules, i.e., Structures, geotechnics, transportation, hydrotechnics and project management. While supporting/interdiscipline subjects are land surveying, computer programmeming and application, civil engineering drawing, engineering mathematics, statistic for civil engineering, system modeling for civil engineering. Minimum 3 out of 24 elective subjects can be taken by students start from semester 5 to support final project topic of interest (classification of elective subjects related to the final project topic). These elective courses allow students to attend classes in accordance with their needs to support their specialised skills and knowledge. The course structures in a bachelor programme is summarized in Table below.
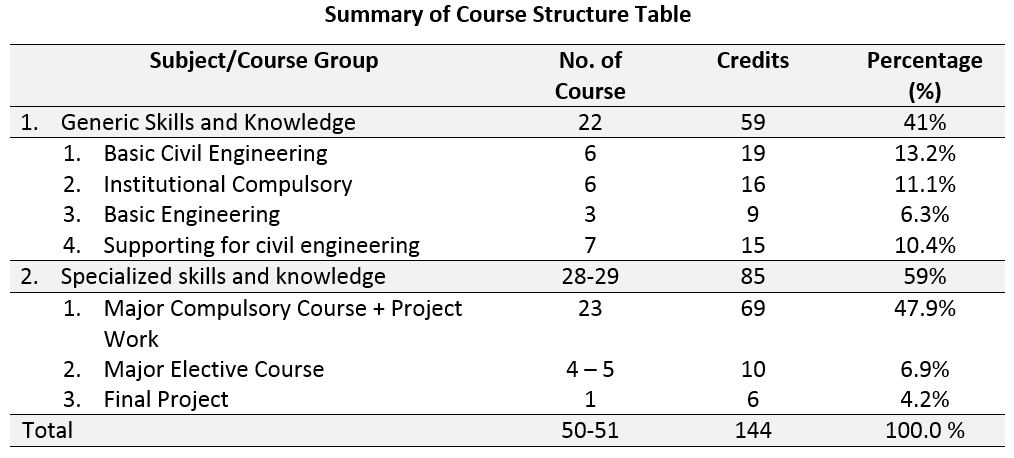
An educational system is expressed by Semester Credit System (Sistem Kredit Semester – SKS), which is defined as a system of education with semester credit units (credits) to state loads of students, lecturers, and programme implementations per week. One credit is defined as 50 minutes’ lecture, 50-100 minutes structured academic activities, and 50-100 minutes independent learning activities. Semester is a unit of time for teaching and learning activities, equal to 16 (sixteen) weeks of classes or other scheduled activities including evaluation. Summary of programme related to course credits and level of studies are presented in Table below.