The QS World University Rankings continue to enjoy a remarkably consistent methodological framework, compiled using six simple metrics that we believe effectively capture university performance. Since faculty area normalisation was introduced in 2015 to ensure that institutions specialising in Life Sciences and Natural Sciences were not unduly advantaged, we have avoided fundamental changes. In doing so, we aim to ensure that year-on-year comparisons remain valid, and that unnecessary volatility is minimised.
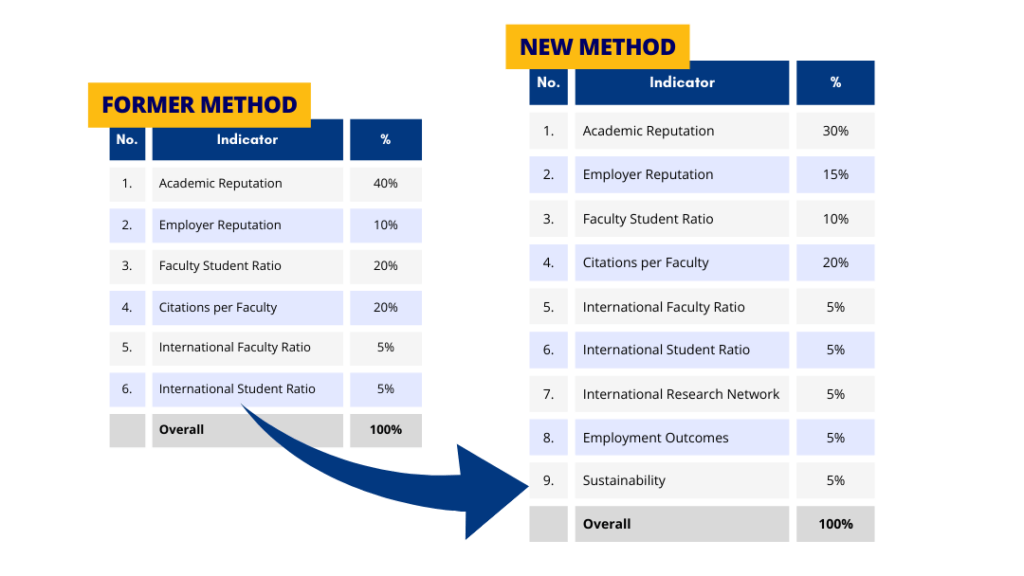
As of 2023, the QS has introduced a new methodology being used compared to the previous years. The change from the previous to the new ones lies in additional metrics. In the previous method, there are only six metrics identified: Academic Reputation, Employer Reputation, Faculty Student Ratio, Citations per Faculty, International Faculty Ratio, and International Student Ratio.
Meanwhile, the most updated method has three additional metrics: International Research Network, Employment Outcomes, and Sustainability. Therefore, nine metrics in total for the QS World University Ranking 2023 are being used. Since there are three additional metrics, it certainly affects the composition of weighting or percentage used for each component. The following figure illustrates the distinction between the former and the new methodology: